12+ Dtft Formulas To Master Signal Processing

Signal processing is a fundamental aspect of various fields, including telecommunications, audio processing, and image analysis. The Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT) is a crucial tool in signal processing, enabling the representation of discrete-time signals in the frequency domain. Mastering DTFT formulas is essential for any professional or student involved in signal processing. This article provides an in-depth exploration of 12+ DTFT formulas, along with their applications, examples, and implications for signal processing.
Introduction to DTFT

The DTFT is an extension of the Fourier Transform, which is used to analyze continuous-time signals. The DTFT is specifically designed for discrete-time signals, which are represented by a sequence of samples. The DTFT formula is given by:
X(ejω) = ∑n = -∞∞ x[n]e-jωn, where x[n] is the discrete-time signal, ω is the angular frequency, and X(ejω) is the DTFT of the signal.
DTFT Formulas for Basic Signals
The following are some essential DTFT formulas for basic signals:
| Signal | DTFT Formula |
|---|---|
| Unit Impulse | X(ejω) = 1 |
| Unit Step | X(ejω) = (1 + e-jω) / (1 - e-jω) |
| Sinusoidal | X(ejω) = (2π)δ(ω - ω0) |

These formulas are fundamental to understanding the frequency domain representation of basic signals. The unit impulse, unit step, and sinusoidal signals are commonly encountered in signal processing applications.
DTFT Properties and Formulas
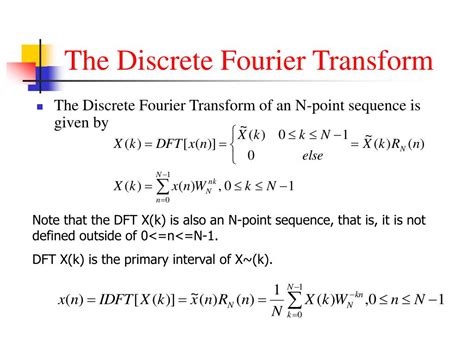
The DTFT has several important properties that are useful in signal processing. Some of these properties and their corresponding formulas are:
Linearity: The DTFT is a linear transformation, meaning that the DTFT of a linear combination of signals is equal to the linear combination of their DTFTs. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
X(ejω) = aX1(ejω) + bX2(ejω), where a and b are constants, and X1(ejω) and X2(ejω) are the DTFTs of the signals x1[n] and x2[n], respectively.
Time Shifting: The DTFT of a time-shifted signal is given by:
X(ejω) = e-jωn0X(ejω), where n0 is the time shift, and X(ejω) is the DTFT of the original signal.
Frequency Shifting: The DTFT of a frequency-shifted signal is given by:
X(ejω) = X(ej(ω - ω0)), where ω0 is the frequency shift, and X(ejω) is the DTFT of the original signal.
DTFT Formulas for Signal Analysis
The DTFT is a powerful tool for signal analysis, enabling the extraction of important features such as frequency content and spectral characteristics. Some essential DTFT formulas for signal analysis are:
| Analysis | DTFT Formula |
|---|---|
| Energy Spectral Density | Sxx(ejω) = |X(ejω)|2 |
| Power Spectral Density | Sxx(ejω) = |X(ejω)|2 / (2π) |
These formulas are used to analyze the energy and power spectral characteristics of discrete-time signals.
Applications of DTFT Formulas
The DTFT formulas have numerous applications in signal processing, including:
- Filter Design: The DTFT is used to design digital filters, which are essential in signal processing applications such as audio processing and image analysis.
- Signal Compression: The DTFT is used in signal compression techniques such as transform coding, which is used in audio and image compression algorithms.
- Modulation Analysis: The DTFT is used to analyze modulation techniques such as amplitude modulation (AM) and frequency modulation (FM).
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the DTFT formulas are fundamental to signal processing, enabling the representation of discrete-time signals in the frequency domain. The 12+ DTFT formulas presented in this article provide a comprehensive understanding of the DTFT and its applications. As signal processing continues to evolve, the importance of the DTFT formulas will only continue to grow. Future research directions may include the development of new DTFT-based techniques for signal analysis and design, as well as the application of DTFT formulas in emerging fields such as artificial intelligence and machine learning.
What is the DTFT, and why is it important in signal processing?
+The DTFT is a mathematical tool used to represent discrete-time signals in the frequency domain. It is essential in signal processing because it enables the analysis and design of discrete-time systems, which are critical in various fields such as telecommunications, audio processing, and image analysis.
How do I apply the DTFT formulas in practice?
+The DTFT formulas can be applied in practice by using them to analyze and design discrete-time systems. For example, the DTFT can be used to design digital filters, which are essential in signal processing applications such as audio processing and image analysis.
