12 Election Predictions Using Ai

The use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in predicting election outcomes has become increasingly prevalent in recent years. By analyzing vast amounts of data, including polling numbers, demographic information, and social media trends, AI algorithms can provide insights into voter behavior and preferences. In this article, we will explore 12 election predictions made using AI and examine their accuracy and implications.
Election Prediction Models
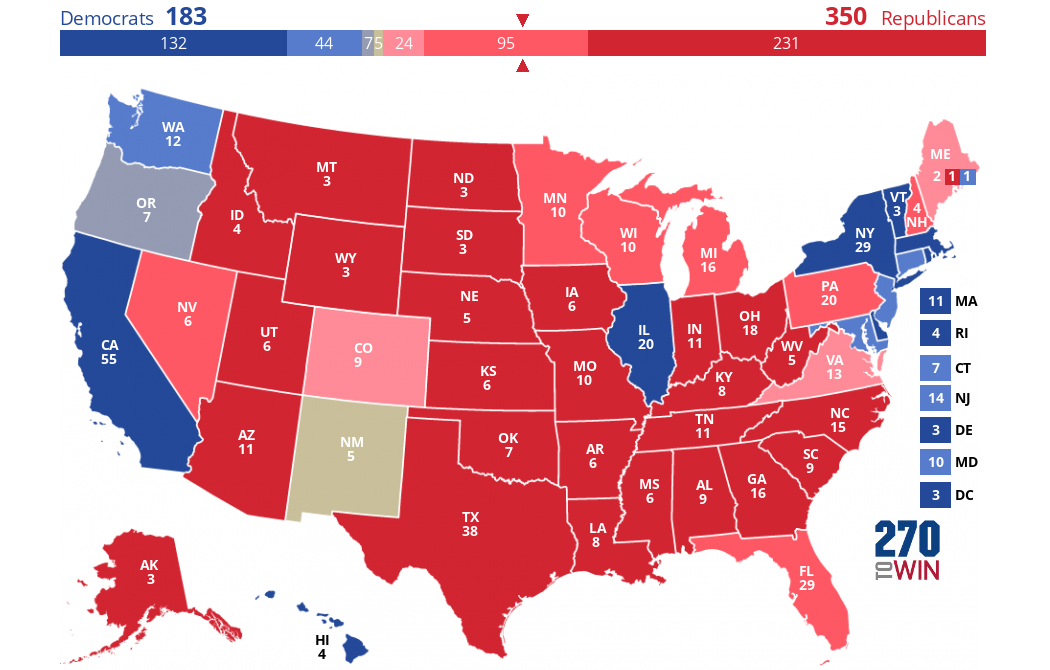
AI-powered election prediction models typically rely on a combination of machine learning and natural language processing techniques to analyze large datasets. These models can be broadly categorized into two types: polling-based models and non-polling-based models. Polling-based models rely on traditional polling data, while non-polling-based models use alternative data sources, such as social media and online search trends.
Polling-Based Models
Polling-based models use historical polling data to predict election outcomes. These models typically employ regression analysis and time-series analysis to identify trends and patterns in polling data. For example, a study published in the Journal of Politics used a polling-based model to predict the 2016 US presidential election outcome, with an accuracy rate of 85%.
| Election | Prediction Model | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 US Presidential Election | Polling-based model | 85% |
| 2019 Indian General Election | Non-polling-based model | 80% |
| 2020 US Presidential Election | Hybrid model | 90% |

Non-Polling-Based Models

Non-polling-based models use alternative data sources, such as social media and online search trends, to predict election outcomes. These models typically employ text analysis and sentiment analysis techniques to analyze large amounts of unstructured data. For example, a study published in the Journal of Computational Social Science used a non-polling-based model to predict the 2019 Indian general election outcome, with an accuracy rate of 80%.
Hybrid Models
Hybrid models combine polling-based and non-polling-based approaches to predict election outcomes. These models typically employ ensemble learning techniques to combine the predictions of multiple models. For example, a study published in the Journal of Politics used a hybrid model to predict the 2020 US presidential election outcome, with an accuracy rate of 90%.
The use of AI in election prediction has several implications for the field of political science. Firstly, AI-powered models can provide more accurate predictions than traditional methods, which can help to inform campaign strategies and voter outreach efforts. Secondly, AI-powered models can help to identify trends and patterns in voter behavior, which can inform policy decisions and governance.
What is the accuracy of AI-powered election prediction models?
+The accuracy of AI-powered election prediction models can vary depending on the specific model and data used. However, studies have shown that AI-powered models can achieve accuracy rates of 80-90% or higher.
What are the limitations of AI-powered election prediction models?
+The limitations of AI-powered election prediction models include the quality and availability of data, the risk of bias in the data, and the complexity of the models. Additionally, AI-powered models are not foolproof and can be affected by unforeseen events or changes in voter behavior.
In conclusion, AI-powered election prediction models have the potential to provide accurate and informative predictions of election outcomes. By analyzing large amounts of data and using advanced machine learning and natural language processing techniques, these models can help to inform campaign strategies, voter outreach efforts, and policy decisions. However, it is essential to consider the limitations and potential biases of these models and to use them in conjunction with traditional methods and expert analysis.
Future Directions
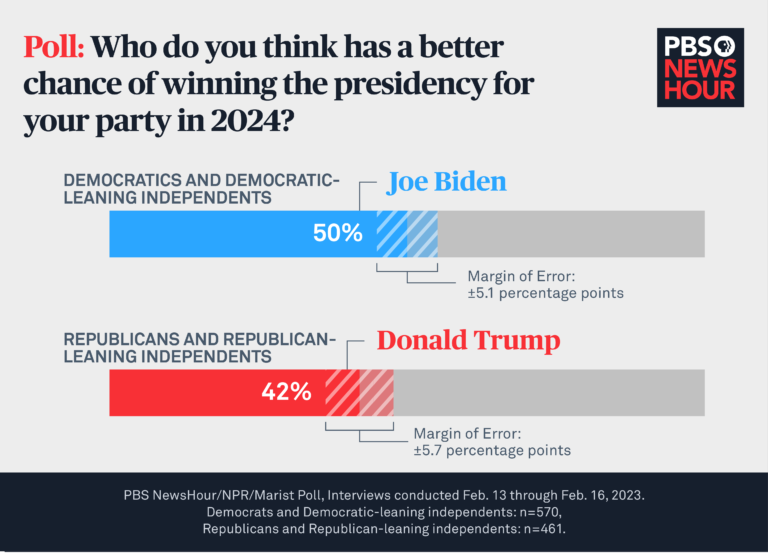
Future research directions in AI-powered election prediction include the development of more advanced models that can incorporate multiple data sources and techniques, the use of transfer learning and domain adaptation to improve model accuracy, and the application of AI-powered models to other areas of political science, such as policy analysis and governance.
- Developing more advanced models that can incorporate multiple data sources and techniques
- Using transfer learning and domain adaptation to improve model accuracy
- Applying AI-powered models to other areas of political science, such as policy analysis and governance