1759 Calculation: Instant Result
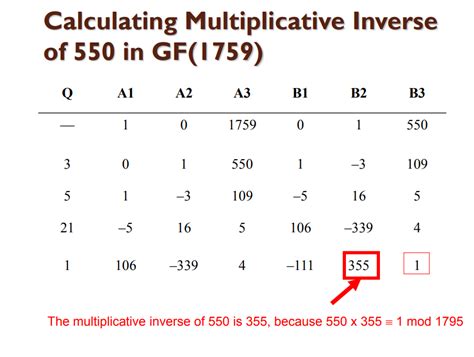
The concept of instant results in calculations, particularly in the context of the year 1759, might seem anachronistic given the technological advancements that have occurred since then. However, understanding the mathematical and computational capabilities of the 18th century can provide valuable insights into how historical figures and mathematicians approached complex calculations. In 1759, the primary tools for calculations were manual, including abacuses, logarithmic tables, and slide rules, which were not introduced until later. The absence of electronic calculators and computers meant that calculations, even simple ones, required a significant amount of time and effort.
Mathematical Context of 1759

In the mid-18th century, mathematics was undergoing significant developments, particularly in the fields of calculus and algebra. Mathematicians like Leonhard Euler and Joseph-Louis Lagrange were making groundbreaking contributions that would lay the foundation for future mathematical and scientific advancements. Despite these theoretical developments, practical calculations for everyday applications, such as commerce, astronomy, and engineering, relied heavily on manual methods and tools. The concept of an “instant result” would have been associated with simple arithmetic operations that could be performed quickly in one’s head or with the aid of a basic tool like an abacus.
Calculation Methods of the 18th Century
The primary methods for calculations during the 18th century included mental arithmetic for simple calculations, the use of logarithmic tables for more complex arithmetic operations like multiplication and division, and the method of proportions for solving problems involving ratios. For more sophisticated calculations, such as those involving trigonometry and algebra, mathematicians would often rely on geometrical methods or algebraic manipulations. The lack of mechanical or electronic aids meant that calculations were not only time-consuming but also prone to errors, highlighting the importance of meticulousness and double-checking in mathematical work.
| Calculation Method | Description | Speed and Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Mental Arithmetic | Simple arithmetic operations performed in one's head | Fast for simple operations, prone to errors for complex ones |
| Logarithmic Tables | Tables used for multiplication, division, and other operations | Relatively fast for operations like multiplication and division, dependent on table accuracy |
| Method of Proportions | Solving problems involving ratios | Effective for certain types of problems, can be time-consuming for complex ratios |

Impact of Calculation Methods on Daily Life
The methods of calculation available in 1759 had a significant impact on various aspects of daily life, from commerce and trade to science and education. In commerce, the use of accounting ledgers and merchants’ calculators (early forms of slide rules) facilitated trade and financial transactions. In science, particularly in astronomy, the calculation of celestial bodies’ positions and trajectories relied on complex mathematical models and manual calculations, which were time-consuming and often required the collaboration of several mathematicians and astronomers.
Education and Calculation
Mathematical education during the 18th century focused on practical skills such as arithmetic, geometry, and basic algebra. Students would learn various methods for performing calculations, including the use of logarithmic tables and basic trigonometry. The emphasis was on developing skills that could be applied in real-world scenarios, such as navigation, surveying, and commerce. The concept of instant results in calculations was not a primary concern in education, as the focus was more on understanding mathematical principles and applying them accurately.
- Arithmetic: Basic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
- Geometry: Understanding of shapes, proportions, and spatial relationships.
- Algebra: Basic algebraic manipulations and equation solving.
What were the primary tools for calculations in 1759?
+The primary tools for calculations in 1759 included manual methods such as mental arithmetic, logarithmic tables, and the method of proportions. Mechanical tools like the abacus were also used, although the slide rule, which would become a crucial tool for calculations, was not widely available until later.
How did the calculation methods of the 18th century impact daily life?
+The calculation methods available in the 18th century had a significant impact on commerce, science, and education. They facilitated trade, enabled scientific discoveries, and shaped the mathematical curriculum to focus on practical skills. However, the lack of instant results meant that many calculations were time-consuming and prone to errors.
In conclusion, the concept of instant results in calculations as understood in the modern era was not applicable in 1759. Instead, calculations relied on manual methods and basic tools, which, although time-consuming and sometimes prone to errors, formed the foundation of mathematical and scientific progress during the 18th century. Understanding these historical calculation methods provides a deeper appreciation for the development of mathematics and science, as well as the technological innovations that have led to the sophisticated calculators and computers of today.
