7 Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium Secrets Uncovered

The pseudostratified columnar epithelium is a type of epithelial tissue that appears to be layered due to the varying heights of its cells, but is actually a single layer of cells. This unique arrangement allows for a larger surface area, which is crucial for the tissue's functions, including absorption, secretion, and protection. Found in various parts of the body, such as the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts, pseudostratified columnar epithelium plays a vital role in maintaining the body's homeostasis. In this article, we will delve into the structure, functions, and significance of pseudostratified columnar epithelium, uncovering its secrets and exploring its importance in human health.
Structure and Organization
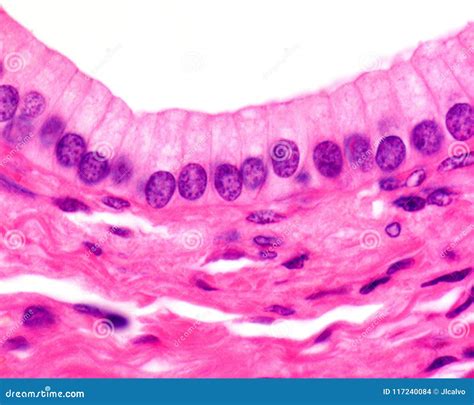
The pseudostratified columnar epithelium is characterized by its columnar cells, which are elongated and prismatic in shape. These cells are arranged in a single layer, but their varying heights give the appearance of multiple layers. The cells are typically attached to a basement membrane, a thin layer of fibrous connective tissue that provides support and separates the epithelium from the underlying tissue. The basal cells, which are the shortest cells in the epithelium, are located near the basement membrane and serve as stem cells, giving rise to new cells through mitosis. The tall cells, on the other hand, are the longest cells and are often ciliated or have microvilli, which increase the surface area for absorption or secretion.
Cell Types and Functions
The pseudostratified columnar epithelium is composed of several cell types, each with unique functions. The ciliated cells have hair-like projections called cilia, which beat in a coordinated manner to move mucus or other substances along the surface of the epithelium. The goblet cells are specialized cells that produce mucus, a thick, protective substance that helps to lubricate and trap pathogens. The basal cells, as mentioned earlier, serve as stem cells, while the tall cells are involved in absorption, secretion, or other specialized functions.
| Cell Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Ciliated cells | Movement of mucus or substances |
| Goblet cells | Mucus production |
| Basal cells | Stem cells, cell renewal |
| Tall cells | Absorption, secretion, or specialized functions |

Functions and Significance

The pseudostratified columnar epithelium plays a vital role in various bodily functions, including respiration, urination, and reproduction**. In the respiratory tract, the epithelium helps to filter, warm, and humidify the air we breathe, while in the urinary tract, it aids in the filtration and excretion of waste products. In the reproductive tract, the epithelium is involved in the production of hormones and the maintenance of a healthy environment for fertilization and implantation.
Clinical Significance
Dysfunction or damage to the pseudostratified columnar epithelium can lead to various health problems, including respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma, urinary tract infections, and reproductive disorders such as infertility. Understanding the structure and functions of this epithelial tissue is essential for the development of effective treatments and therapies for these conditions.
- Respiratory diseases: COPD, asthma
- Urinary tract infections
- Reproductive disorders: infertility
What is the main function of the pseudostratified columnar epithelium in the respiratory tract?
+The main function of the pseudostratified columnar epithelium in the respiratory tract is to filter, warm, and humidify the air we breathe, while also aiding in the removal of pathogens and other foreign substances.
What are the consequences of damage to the pseudostratified columnar epithelium in the urinary tract?
+Damage to the pseudostratified columnar epithelium in the urinary tract can lead to urinary tract infections, kidney damage, and other complications, highlighting the importance of maintaining the health and integrity of this epithelial tissue.
In conclusion, the pseudostratified columnar epithelium is a complex and vital tissue that plays a crucial role in maintaining human health. Its unique structure and cell types allow it to perform a range of functions, from absorption and secretion to protection and movement of substances. Understanding the secrets of this epithelial tissue is essential for appreciating its importance and for the development of effective treatments and therapies for various health conditions.