Blood & Sugar
Blood and sugar, two substances that are intricately linked in the human body, play a crucial role in our overall health and wellbeing. The relationship between blood and sugar is complex, with blood sugar levels being a key indicator of our metabolic health. In this article, we will delve into the world of blood and sugar, exploring the ways in which they interact and the implications of this relationship for our health.
The Basics of Blood Sugar

Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is a type of sugar that is found in the blood. It is the primary source of energy for the body’s cells, and it is obtained from the food we eat. The level of glucose in the blood is regulated by the pancreas, which produces two main hormones: insulin and glucagon. Insulin helps to lower blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells, while glucagon helps to raise blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of glucose from stored energy sources. The balance between these two hormones is crucial for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
The Impact of Diet on Blood Sugar
Diet plays a significant role in determining blood sugar levels. Foods that are high in carbohydrates, such as sugary drinks, white bread, and sweetened yogurts, can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, foods that are high in fiber and protein, such as fruits, vegetables, and lean meats, can help to slow down the digestion and absorption of glucose, resulting in a more gradual increase in blood sugar levels. Understanding the glycemic index of different foods can help individuals make informed choices about their diet and manage their blood sugar levels more effectively.
| Foods | Glycemic Index |
|---|---|
| White bread | 70-80 |
| Brown rice | 50-60 |
| Apple | 30-40 |
| Broccoli | 10-20 |

The Consequences of Unmanaged Blood Sugar
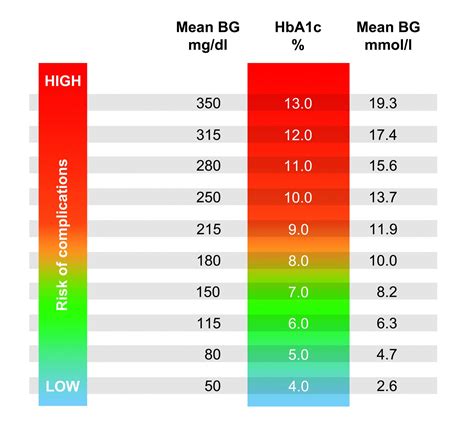
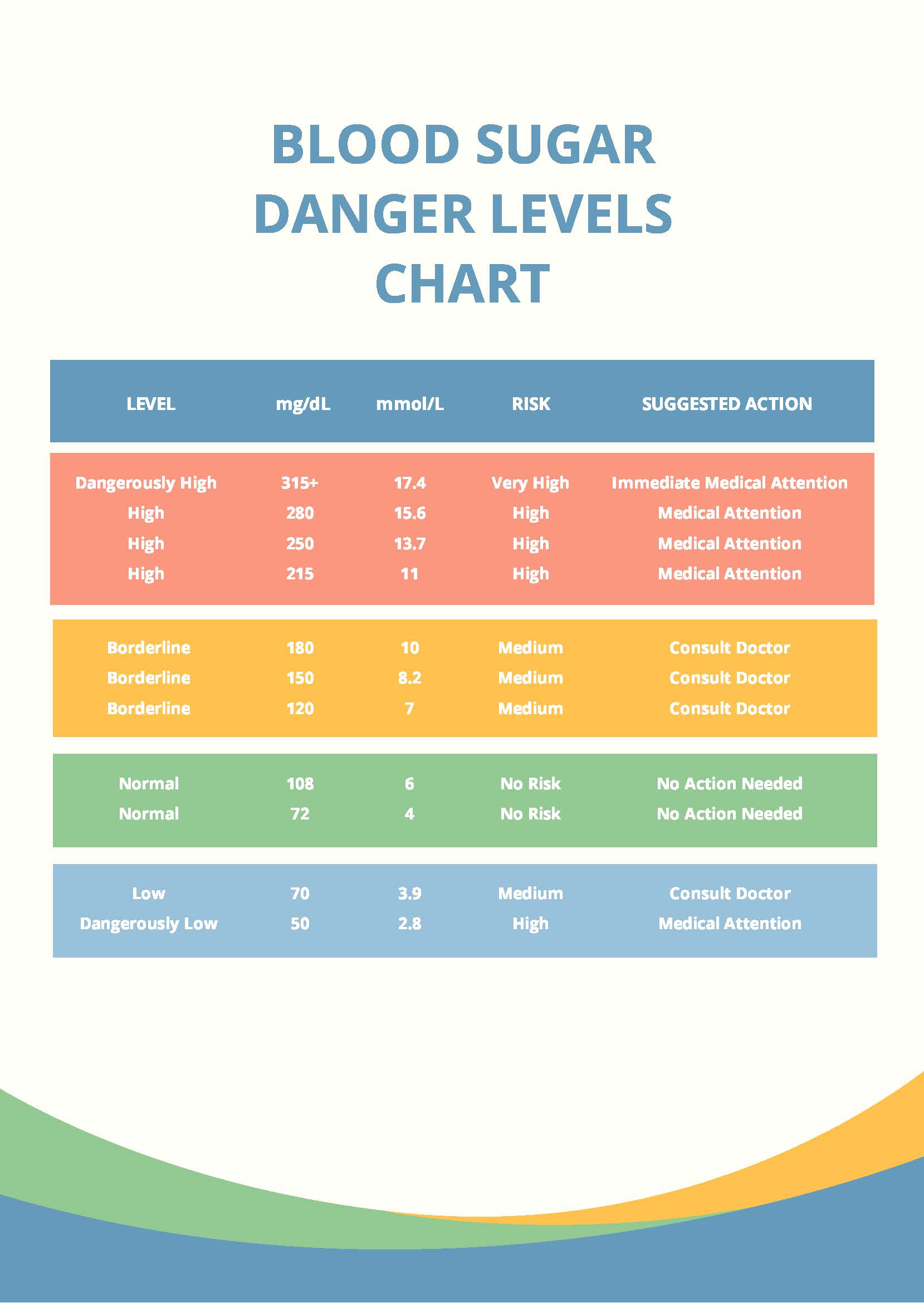
Unmanaged blood sugar levels can have serious consequences for our health. Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, can lead to a range of health problems, including diabetic neuropathy, kidney damage, and blindness. On the other hand, hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can cause symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, and loss of consciousness. It is essential to monitor blood sugar levels regularly and take steps to manage them effectively to prevent these complications.
The Role of Exercise in Managing Blood Sugar
Regular exercise can play a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels. Aerobic exercise, such as walking, cycling, and swimming, can help to improve insulin sensitivity, reducing the amount of insulin needed to regulate blood sugar levels. Resistance training, such as weightlifting, can also help to improve glucose uptake in the muscles, further reducing blood sugar levels. Additionally, high-intensity interval training (HIIT) has been shown to be particularly effective in improving insulin sensitivity and reducing blood sugar levels.
- Aerobic exercise: 150 minutes/week
- Resistance training: 2-3 sessions/week
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT): 2-3 sessions/week
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
+The symptoms of high blood sugar include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds. If left untreated, high blood sugar can lead to more serious health problems, such as diabetic neuropathy, kidney damage, and blindness.
How can I lower my blood sugar levels?
+To lower your blood sugar levels, focus on making healthy lifestyle changes, such as eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar and refined carbohydrates, exercising regularly, and getting enough sleep. Additionally, consider working with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized plan for managing your blood sugar levels.
In conclusion, the relationship between blood and sugar is complex and multifaceted. By understanding how blood sugar levels are regulated and the factors that influence them, individuals can take steps to manage their blood sugar levels effectively and reduce their risk of developing related health problems. With the right combination of diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes, it is possible to maintain healthy blood sugar levels and promote overall health and wellbeing.
