Convert 5 Minutes: Decimal Made Simple
Understanding decimals is a fundamental aspect of mathematics, and it can be made simple with the right approach. Decimals are a way of representing fractions using a point, and they are widely used in everyday life, from measuring ingredients for cooking to calculating financial transactions. In this explanation, we will delve into the world of decimals, exploring what they are, how to convert fractions to decimals, and how to perform operations with decimals.
Introduction to Decimals
Decimals are a type of number that has a whole part and a fractional part. The whole part is the part before the decimal point, and the fractional part is the part after the decimal point. For example, in the number 12.45, 12 is the whole part, and 0.45 is the fractional part. Decimals are used to represent numbers that are not whole, and they are essential in many areas of mathematics and real-life applications.
Understanding Decimal Places
A decimal place is the position of a digit in a decimal number. The decimal places are counted from the decimal point, starting with the first digit after the decimal point as the tenths place, the second digit as the hundredths place, and so on. For example, in the number 12.456, the 4 is in the tenths place, the 5 is in the hundredths place, and the 6 is in the thousandths place. Understanding decimal places is crucial for performing operations with decimals and for converting fractions to decimals.
| Decimal Place | Description |
|---|---|
| Tenths | The first digit after the decimal point |
| Hundredths | The second digit after the decimal point |
| Thousandths | The third digit after the decimal point |
Decimals can be classified into different types, including terminating decimals, which have a finite number of digits after the decimal point, and non-terminating decimals, which have an infinite number of digits after the decimal point. Understanding these types of decimals is essential for working with decimals in mathematics and real-life applications.
Converting Fractions to Decimals
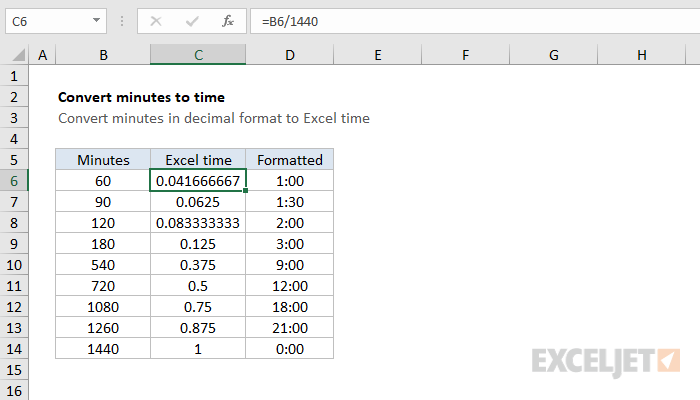
Converting fractions to decimals is a straightforward process that involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. For example, to convert the fraction 3⁄4 to a decimal, we divide 3 by 4, which gives us 0.75. This process can be applied to any fraction, and it is an essential skill for working with decimals in mathematics and real-life applications.
Converting Improper Fractions to Decimals
Improper fractions are fractions where the numerator is greater than the denominator. Converting improper fractions to decimals involves dividing the numerator by the denominator, just like with proper fractions. For example, to convert the improper fraction 5⁄4 to a decimal, we divide 5 by 4, which gives us 1.25.
It's worth noting that some fractions cannot be converted to decimals exactly, and they are known as non-terminating decimals. These fractions have an infinite number of digits after the decimal point, and they are often represented using a repeating pattern of digits. For example, the fraction 1/3 is a non-terminating decimal, and it is often represented as 0.333..., where the 3 repeats infinitely.
| Fraction | Decimal Equivalent |
|---|---|
| 1/2 | 0.5 |
| 1/4 | 0.25 |
| 3/4 | 0.75 |
Performing Operations with Decimals

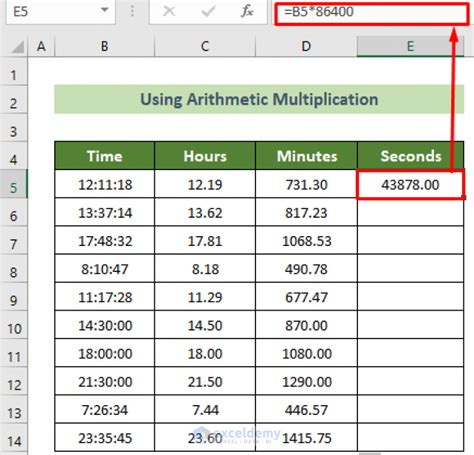
Performing operations with decimals involves applying the same rules as with whole numbers, with the added consideration of the decimal point. When adding or subtracting decimals, the decimal points must be aligned, and the numbers must be added or subtracted as with whole numbers. When multiplying decimals, the decimal point is placed in the product by counting the total number of decimal places in the factors. When dividing decimals, the divisor is converted to a whole number by moving the decimal point to the right, and the dividend is converted to a whole number by moving the decimal point to the right by the same number of places.
Adding and Subtracting Decimals
Adding and subtracting decimals involves aligning the decimal points and adding or subtracting the numbers as with whole numbers. For example, to add 2.5 and 1.8, we align the decimal points and add the numbers, which gives us 4.3.
When subtracting decimals, we follow the same process, aligning the decimal points and subtracting the numbers as with whole numbers. For example, to subtract 1.8 from 2.5, we align the decimal points and subtract the numbers, which gives us 0.7.
| Operation | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Addition | 2.5 + 1.8 | 4.3 |
| Subtraction | 2.5 - 1.8 | 0.7 |
What is a decimal?
+A decimal is a type of number that has a whole part and a fractional part, represented using a point.
How do I convert a fraction to a decimal?
+To convert a fraction to a decimal, divide the numerator by the denominator.
What is the difference between a terminating decimal and a non-terminating decimal?
+A terminating decimal has a finite number of digits after the decimal point, while a non-terminating decimal has an infinite number of digits after the decimal point.