Gene Disease Causal Inference

Gene disease causal inference is a critical aspect of modern genetics and genomics, aiming to identify the causal relationships between genetic variations and diseases. This field has gained significant attention in recent years due to the increasing availability of large-scale genomic data and the development of sophisticated computational methods. The primary goal of gene disease causal inference is to pinpoint the specific genes and genetic variants that contribute to the development and progression of complex diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
Introduction to Gene Disease Causal Inference
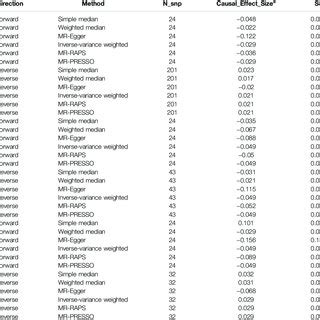
Gene disease causal inference involves the use of statistical and computational approaches to analyze the associations between genetic variants and disease phenotypes. The process typically begins with the collection of genomic data from large cohorts of individuals, followed by the application of various analytical techniques to identify significant associations between genetic variants and disease traits. However, establishing causality is a challenging task, as it requires the consideration of multiple factors, including the direction of causality, confounding variables, and the presence of multiple causal variants.
Challenges in Gene Disease Causal Inference
One of the major challenges in gene disease causal inference is the distinction between correlation and causation. While genetic variants may be associated with a particular disease, it is essential to determine whether these variants are the cause of the disease or simply correlated with other causal factors. Confounding variables, such as environmental factors and demographic characteristics, can also influence the relationship between genetic variants and disease traits, making it difficult to establish causality. Furthermore, pleiotropy, the phenomenon where a single gene affects multiple traits, can complicate the analysis of gene disease relationships.
| Challenges in Gene Disease Causal Inference | Description |
|---|---|
| Correlation vs. Causation | Distinguishing between genetic variants that are correlated with disease traits and those that are causal |
| Confounding Variables | Accounting for environmental and demographic factors that influence the relationship between genetic variants and disease traits |
| Pleiotropy | Dealing with the phenomenon where a single gene affects multiple traits, complicating the analysis of gene disease relationships |
Methods for Gene Disease Causal Inference

Several methods have been developed to infer causal relationships between genetic variants and disease traits. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) are widely used to identify genetic variants associated with disease traits, while functional genomics approaches, such as gene expression analysis and chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq), provide insights into the functional consequences of genetic variants. Additionally, machine learning algorithms, such as random forests and neural networks, can be applied to integrate multiple data types and predict causal relationships.
Applications of Gene Disease Causal Inference
The applications of gene disease causal inference are numerous and significant. By identifying the causal genetic variants underlying complex diseases, researchers can develop targeted therapies and improve disease diagnosis. Furthermore, gene disease causal inference can inform personalized medicine approaches, enabling clinicians to tailor treatment strategies to an individual’s unique genetic profile. The insights gained from gene disease causal inference can also be used to develop predictive models for disease risk and progression.
- Developing targeted therapies for complex diseases
- Improving disease diagnosis and prognosis
- Informing personalized medicine approaches
- Developing predictive models for disease risk and progression
What is the primary goal of gene disease causal inference?
+The primary goal of gene disease causal inference is to identify the causal relationships between genetic variants and disease traits, with the ultimate aim of developing targeted therapies and improving disease diagnosis.
What are some challenges in gene disease causal inference?
+Some challenges in gene disease causal inference include distinguishing between correlation and causation, accounting for confounding variables, and dealing with pleiotropy.
In conclusion, gene disease causal inference is a complex and challenging field that requires the integration of multiple data types and the application of sophisticated computational methods. By addressing the challenges and limitations of gene disease causal inference, researchers can uncover the underlying causal relationships between genetic variants and disease traits, ultimately leading to the development of targeted therapies and improved disease diagnosis.

