History Timeline Of Forensics

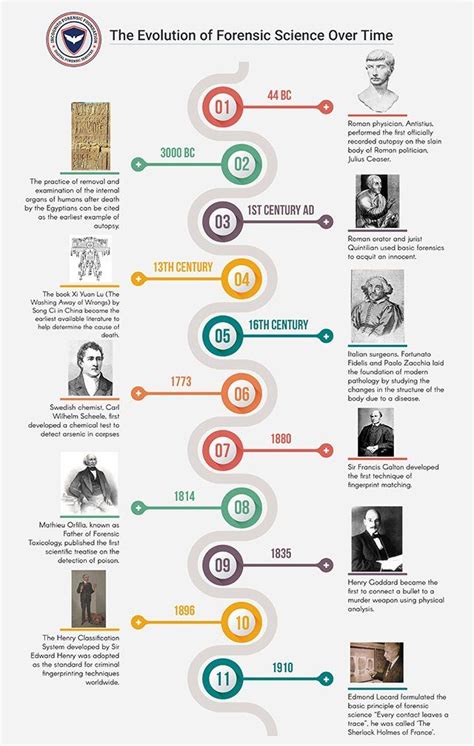
The history of forensics is a rich and complex one, spanning thousands of years and involving the contributions of numerous scientists, investigators, and legal professionals. From ancient civilizations to modern times, the field of forensics has evolved significantly, shaped by advances in technology, changes in societal values, and the development of new methodologies. In this comprehensive timeline, we will explore the major milestones and breakthroughs in the history of forensics, highlighting the key figures, events, and discoveries that have helped shape the field into what it is today.
Ancient Civilizations and the Emergence of Forensics

The earliest recorded evidence of forensic practices dates back to ancient China, where the Xi Yuan Lu, a book on forensic medicine, was written in the 13th century. This text described various methods for examining corpses and determining cause of death, including the use of autopsy and toxicology. Similarly, in ancient Greece and Rome, physicians and philosophers such as Galen and Cicero wrote about the importance of forensic examination in resolving legal disputes. The Edwin Smith Papyrus, an ancient Egyptian medical text, also contains descriptions of forensic examinations and treatments for injuries.
Medieval and Early Modern Periods
During the Middle Ages, the study of forensics continued to evolve, with the establishment of medical schools and the development of new anatomical techniques. The work of Andreas Vesalius, a Flemish anatomist, was particularly influential, as his detailed descriptions of the human body helped lay the foundation for modern forensic pathology. In the 17th and 18th centuries, the use of chemical analysis and microscopy became more widespread, allowing investigators to analyze evidence and identify causes of death with greater accuracy.
| Time Period | Key Developments |
|---|---|
| Ancient China (13th century) | Xi Yuan Lu, forensic medicine text |
| Ancient Greece and Rome (5th century BCE - 5th century CE) | Galen, Cicero, and the Edwin Smith Papyrus |
| Medieval Period (12th - 15th centuries) | Establishment of medical schools, anatomical techniques |
| Early Modern Period (16th - 18th centuries) | Chemical analysis, microscopy, Andreas Vesalius |
The Modern Era of Forensics
The 19th and 20th centuries saw significant advances in forensic science, with the development of new techniques and technologies. The discovery of fingerprinting by Francis Galton in the late 19th century revolutionized the field, allowing investigators to identify individuals with greater accuracy. The establishment of crime labs and the development of forensic psychology also played important roles in shaping the modern field of forensics.
Key Figures and Developments
One of the most influential figures in the history of forensics is Edmond Locard, a French criminologist who established the first crime lab in 1910. Locard’s work on hair analysis and footwear impressions helped lay the foundation for modern forensic science. Other key figures include Calvin Goddard, who developed the first ballistics lab, and Alexander O. Gettler, who pioneered the use of toxicology in forensic investigations.
- Fingerprinting: developed by Francis Galton in the late 19th century
- Crime labs: established in the early 20th century
- Forensic psychology: developed in the mid-20th century
- Edmond Locard: established the first crime lab in 1910
- Calvin Goddard: developed the first ballistics lab
- Alexander O. Gettler: pioneered the use of toxicology in forensic investigations
What is the significance of the Xi Yuan Lu in the history of forensics?
+The Xi Yuan Lu is a medieval Chinese text that describes various methods for examining corpses and determining cause of death. It is considered one of the earliest recorded examples of forensic medicine and demonstrates the importance of forensic examination in ancient Chinese society.
How has the development of DNA analysis impacted the field of forensics?
+The development of DNA analysis has revolutionized the field of forensics, allowing investigators to identify individuals and analyze evidence with greater accuracy. DNA analysis has been used in a wide range of applications, from paternity testing to crime scene investigation.
In conclusion, the history of forensics is a complex and fascinating field that has evolved significantly over time. From ancient civilizations to modern times, the development of new techniques and technologies has helped shape the field into what it is today. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that the field of forensics will continue to evolve, incorporating new methodologies and techniques to help investigators solve crimes and resolve legal disputes.


