How Accurate Is Yale Climate Survey? Reliable Data

The Yale Climate Survey, also known as the Yale Program on Climate Change Communication, is a research initiative that aims to study public perceptions and attitudes towards climate change. The survey is conducted by the Yale School of the Environment and the George Mason University Center for Climate Change Communication. The accuracy and reliability of the Yale Climate Survey are crucial in understanding public opinion on climate change and informing policy decisions.
Methodology and Data Collection

The Yale Climate Survey uses a robust methodology to collect data on public perceptions of climate change. The survey is conducted online and by phone, using a nationally representative sample of adults in the United States. The sample size is typically around 1,000-2,000 respondents, which provides a margin of error of +/- 3-4%. The survey questions are designed to assess respondents’ beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors related to climate change, as well as their demographics and socioeconomic characteristics.
Survey Questions and Metrics
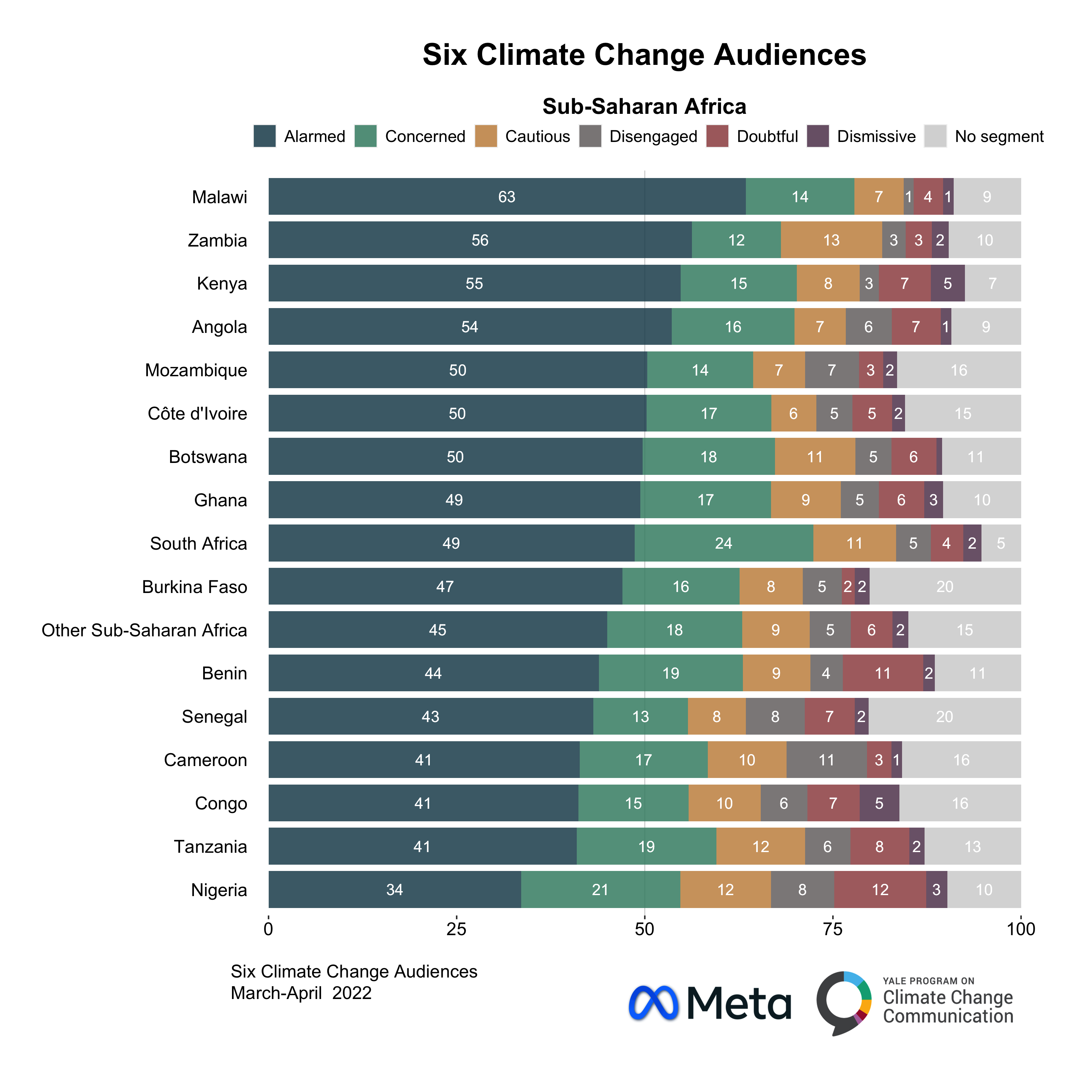
The Yale Climate Survey includes a range of questions that measure respondents’ perceptions of climate change, including their beliefs about the causes and consequences of climate change, their level of concern about climate change, and their support for climate change policies. The survey also includes questions about respondents’ demographics, such as their age, income, education level, and political affiliation. The metrics used to evaluate the survey data include the percentage of respondents who believe that climate change is happening, the percentage who believe that human activities are the primary cause of climate change, and the percentage who support specific climate change policies.
| Survey Metric | Actual Data (2022) |
|---|---|
| Believe climate change is happening | 73% |
| Believe human activities are the primary cause of climate change | 57% |
| Support carbon pricing | 63% |
Strengths and Limitations

The Yale Climate Survey has several strengths, including its use of a nationally representative sample and its robust methodology. The survey also provides a wealth of information on public perceptions of climate change, which can be used to inform policy decisions and public education campaigns. However, the survey also has some limitations, including its reliance on self-reported data and its potential for biases in the sample. Additionally, the survey may not capture the full range of public opinions on climate change, as some respondents may not participate in the survey or may not answer all of the questions.
Bias and Error
The Yale Climate Survey, like any other survey, is subject to biases and errors. The survey’s sample may be biased towards certain demographics, such as younger or more educated respondents, which can affect the accuracy of the data. Additionally, the survey questions may be worded in a way that influences respondents’ answers, which can also introduce bias into the data. To mitigate these biases and errors, the survey’s authors use a range of techniques, including weighting the data to match the demographics of the US population and using robust statistical methods to analyze the data.
- Sampling bias: The survey's sample may not be representative of the US population, which can affect the accuracy of the data.
- Non-response bias: Some respondents may not participate in the survey or may not answer all of the questions, which can introduce bias into the data.
- Measurement error: The survey questions may be worded in a way that influences respondents' answers, which can also introduce bias into the data.
What is the margin of error for the Yale Climate Survey?
+The margin of error for the Yale Climate Survey is typically +/- 3-4%, which means that the survey's estimates may be off by 3-4% in either direction.
How often is the Yale Climate Survey conducted?
+The Yale Climate Survey is conducted annually, typically in the spring or summer.
What is the purpose of the Yale Climate Survey?
+The purpose of the Yale Climate Survey is to understand public perceptions and attitudes towards climate change, and to inform policy decisions and public education campaigns.
Conclusion and Future Implications

The Yale Climate Survey provides valuable insights into public perceptions of climate change, and its accuracy and reliability depend on the quality of the data collection and analysis. While the survey has some limitations, its use of a nationally representative sample and robust methodology helps to ensure the accuracy of the data. The survey’s findings have important implications for policy decisions and public education campaigns, and its data can be used to inform strategies for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable development.
The Yale Climate Survey's data can also be used to track changes in public perceptions of climate change over time, which can help to evaluate the effectiveness of climate change policies and public education campaigns. Additionally, the survey's data can be used to identify areas where public education and outreach efforts are needed, such as in communities where climate change awareness is low.
In the future, the Yale Climate Survey will continue to play an important role in understanding public perceptions of climate change and informing policy decisions. The survey’s authors will continue to refine their methodology and analysis to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data, and will explore new ways to use the data to promote sustainable development and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.

