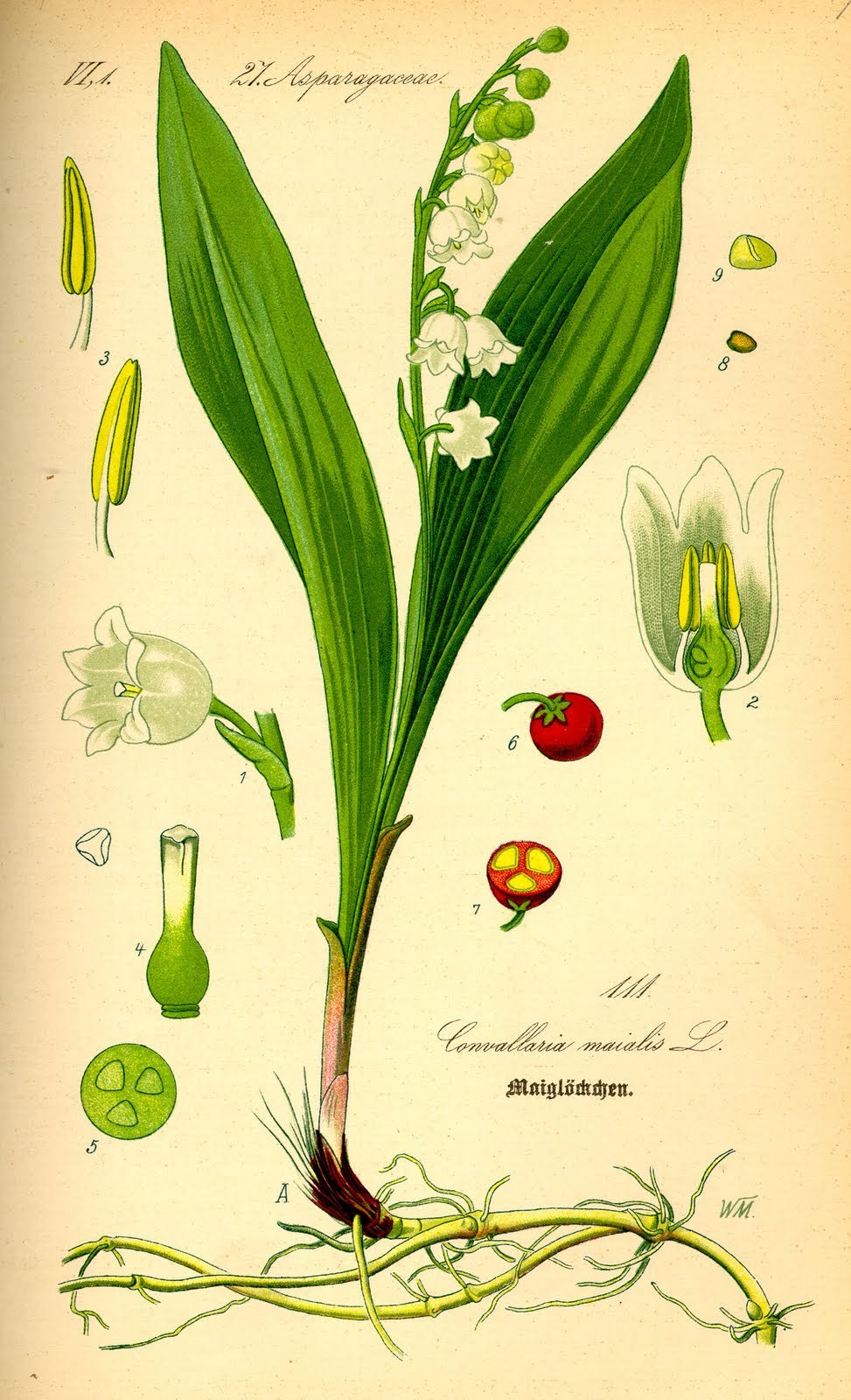
Lily Of The Valley Poison

Lily of the valley (Convallaria majalis) is a perennial plant known for its beautiful, fragrant white flowers and red berries. While it is often used in floral arrangements and as an ornamental plant, it is also highly toxic. The plant contains a group of cardiac glycosides, including convallatoxin, convalloside, and others, which can cause serious health problems if ingested.
Toxicity and Poisoning Symptoms

The toxicity of lily of the valley is due to the presence of cardiac glycosides, which can affect the heart and nervous system. If ingested, the plant can cause a range of symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and headache. In more severe cases, it can lead to cardiac arrhythmias, including bradycardia (slow heart rate) and tachycardia (fast heart rate), as well as hypotension (low blood pressure) and confusion. In extreme cases, ingestion of lily of the valley can be fatal.
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
The clinical presentation of lily of the valley poisoning can vary depending on the amount and part of the plant ingested, as well as the individual’s overall health. Diagnosis is typically made based on a combination of physical examination, laboratory tests, and patient history. Laboratory tests may include electrocardiogram (ECG) to monitor heart rhythm, as well as blood tests to check for signs of cardiac damage or other complications.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Nausea and Vomiting | Gastrointestinal symptoms that can occur within 1-2 hours after ingestion |
| Cardiac Arrhythmias | Abnormal heart rhythms, including bradycardia and tachycardia, that can occur within 2-6 hours after ingestion |
| Hypotension |

Treatment and Management
Treatment for lily of the valley poisoning typically involves supportive care, including monitoring of vital signs, cardiac rhythm, and blood pressure. In some cases, activated charcoal may be administered to help absorb the toxins and reduce their absorption into the bloodstream. Medications such as atropine and lidocaine may be used to manage cardiac arrhythmias and other complications. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide close monitoring and supportive care.
Prevention and Safety Precautions
To prevent lily of the valley poisoning, it is essential to handle the plant with care and avoid ingesting any parts of it. This includes wearing gloves when handling the plant, and washing hands thoroughly after handling. It is also important to keep the plant out of reach of children and pets, and to dispose of any plant parts properly to prevent accidental ingestion.
- Wear gloves when handling lily of the valley
- Wash hands thoroughly after handling the plant
- Keep the plant out of reach of children and pets
- Dispose of any plant parts properly
What should I do if I suspect someone has ingested lily of the valley?
+If you suspect someone has ingested lily of the valley, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. Call your local emergency number or poison control center for guidance and support.
How can I prevent lily of the valley poisoning in my home?
+To prevent lily of the valley poisoning in your home, make sure to handle the plant with care, wear gloves when handling it, and wash your hands thoroughly after handling. Keep the plant out of reach of children and pets, and dispose of any plant parts properly.
In conclusion, lily of the valley is a highly toxic plant that can cause serious health problems if ingested. It is essential to handle the plant with care, avoid ingesting any parts of it, and seek medical attention immediately if you suspect someone has ingested it. By taking these precautions and being aware of the potential risks, you can help prevent lily of the valley poisoning and keep yourself and others safe.