Nanobody's Function In Researching Gpcr
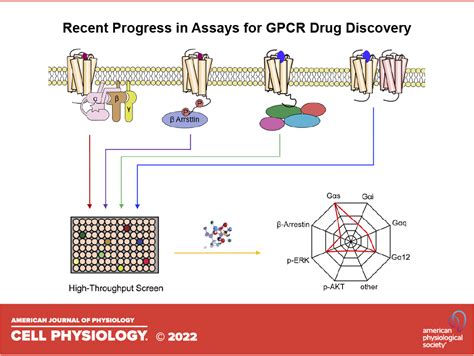
Nanobodies, also known as single-domain antibodies or VHHs, have revolutionized the field of biomedical research, particularly in the study of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). GPCRs are a large family of membrane receptors that play a crucial role in various physiological processes, including signal transduction, cell communication, and regulation of various biological functions. Due to their complex structure and dynamic nature, GPCRs have been challenging to study using traditional biochemical and biophysical methods. However, the advent of nanobodies has provided a powerful tool for researching GPCRs, enabling scientists to gain a deeper understanding of their structure, function, and regulation.
Introduction to Nanobodies and GPCRs

Nanobodies are small, single-domain antibody fragments that are derived from the variable region of heavy-chain-only antibodies found in camelids, such as camels and llamas. They are characterized by their small size, high stability, and ability to bind to specific targets with high affinity and selectivity. GPCRs, on the other hand, are a large family of receptors that respond to a wide range of stimuli, including hormones, neurotransmitters, and light. They are composed of seven transmembrane alpha-helices and are involved in various physiological processes, including signal transduction, cell proliferation, and differentiation.
Advantages of Nanobodies in GPCR Research
Nanobodies offer several advantages in GPCR research, including their small size, high stability, and ability to bind to specific epitopes on the receptor. These characteristics enable nanobodies to access and stabilize specific conformations of GPCRs, allowing researchers to study their structure and function in detail. Additionally, nanobodies can be engineered to have specific properties, such as high affinity, selectivity, and stability, making them ideal tools for GPCR research.
| Advantages of Nanobodies | Description |
|---|---|
| Small size | Enables access to specific epitopes on GPCRs |
| High stability | Allows for long-term storage and handling |
| High affinity and selectivity | Enables specific binding to GPCRs |
| Engineerability | Can be designed to have specific properties |
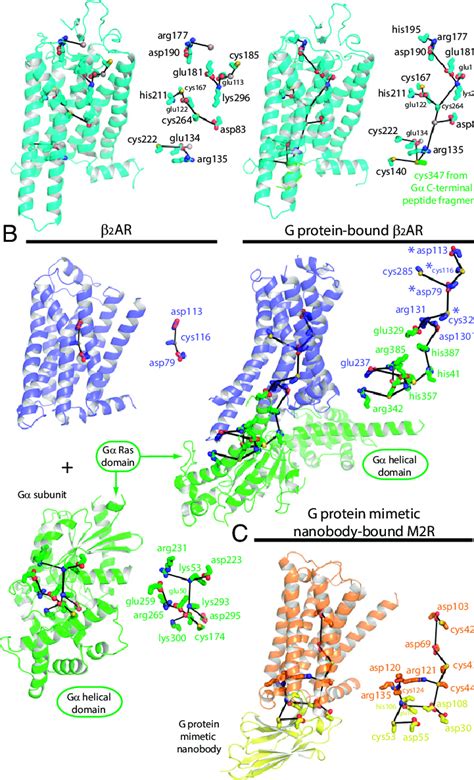
Applications of Nanobodies in GPCR Research

Nanobodies have been widely used in GPCR research, including structural biology, biophysical studies, and functional assays. They have been used to stabilize specific conformations of GPCRs, enabling high-resolution structural studies using techniques such as X-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy. Additionally, nanobodies have been used to study the dynamic behavior of GPCRs, including their conformational changes and interactions with other molecules.
Structural Biology of GPCRs using Nanobodies
Nanobodies have been used to stabilize specific conformations of GPCRs, enabling high-resolution structural studies. For example, nanobodies have been used to stabilize the active conformation of the beta-2 adrenergic receptor, allowing researchers to determine its crystal structure. Additionally, nanobodies have been used to study the structure of GPCRs in complex with other molecules, such as G proteins and beta-arrestins.
| GPCR | Nanobody | Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Beta-2 adrenergic receptor | Nb80 | Active conformation |
| Mu-opioid receptor | Nb39 | Active conformation |
| A2A adenosine receptor | Nb35 | Inactive conformation |
Future Implications of Nanobodies in GPCR Research

The use of nanobodies in GPCR research has significant implications for our understanding of these complex receptors and their role in various physiological processes. The ability to stabilize specific conformations of GPCRs and study their dynamic behavior will enable researchers to develop new therapeutic strategies for the treatment of various diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders. Additionally, the use of nanobodies will enable researchers to study the structure and function of GPCRs in detail, providing valuable insights into their mechanism of action and regulation.
Therapeutic Applications of Nanobodies
Nanobodies have significant therapeutic potential, particularly in the treatment of diseases caused by GPCR dysfunction. For example, nanobodies have been used to develop new therapeutic strategies for the treatment of cancer, including the use of nanobodies that target specific GPCRs involved in tumor growth and metastasis. Additionally, nanobodies have been used to develop new therapeutic strategies for the treatment of neurological disorders, including the use of nanobodies that target specific GPCRs involved in neurotransmission.
What are nanobodies and how do they work?
+Nanobodies are small, single-domain antibody fragments that are derived from the variable region of heavy-chain-only antibodies found in camelids. They work by binding to specific targets, such as GPCRs, with high affinity and selectivity, enabling researchers to study their structure and function in detail.
What are the advantages of using nanobodies in GPCR research?
+The advantages of using nanobodies in GPCR research include their small size, high stability, and ability to bind to specific epitopes on the receptor. These characteristics enable nanobodies to access and stabilize specific conformations of GPCRs, allowing researchers to study their structure and function in detail.
What are the future implications of nanobodies in GPCR research?
+The future implications of nanobodies in GPCR research include the development of new therapeutic strategies for the treatment of various diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders. Additionally, the use of nanobodies will enable researchers to study the structure and function of GPCRs in detail, providing valuable insights into their mechanism of action and regulation.
