Neural Collision Detection Sdf
Neural collision detection using Signed Distance Fields (SDFs) is a cutting-edge technique in the field of computer graphics and robotics. SDFs are a mathematical representation of 3D objects, where each point in space is assigned a signed distance value indicating the distance to the nearest surface. This allows for efficient and accurate collision detection, which is crucial in various applications such as video games, virtual reality, and robotic motion planning.
Introduction to Neural Collision Detection
Traditional collision detection methods rely on discretizing the 3D space into a grid or using complex geometric algorithms to detect intersections. However, these methods can be computationally expensive and may not provide accurate results, especially in complex scenarios. Neural collision detection using SDFs addresses these limitations by leveraging the power of deep learning and the mathematical properties of SDFs. By training a neural network to predict the SDF values for a given 3D scene, it is possible to efficiently and accurately detect collisions.
Mathematical Background of SDFs
SDFs are defined as a function f(x) that maps a 3D point x to a signed distance value. The signed distance value is positive if the point is outside the object, negative if the point is inside the object, and zero if the point is on the surface. This definition allows for the use of SDFs in collision detection, as the signed distance value can be used to determine the proximity of two objects. The mathematical properties of SDFs, such as the ability to compute gradients and normals, make them an attractive choice for neural collision detection.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Signed Distance Value | Indicates the distance to the nearest surface |
| Gradient | Provides the direction of the nearest surface |
| Normal | Provides the orientation of the nearest surface |
Neural Network Architecture
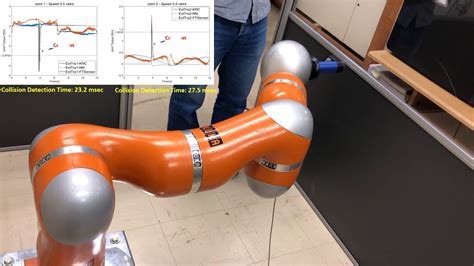
The neural network architecture used for neural collision detection typically consists of a convolutional neural network (CNN) or a fully connected neural network. The input to the network is a 3D point or a set of 3D points, and the output is the predicted SDF value. The network is trained using a dataset of 3D scenes and corresponding SDF values, which can be generated using various methods such as ray marching or sphere tracing.
Training and Optimization
The training process involves optimizing the neural network parameters to minimize the difference between the predicted SDF values and the ground truth values. This can be achieved using various optimization algorithms, such as stochastic gradient descent (SGD) or Adam. The choice of optimization algorithm and hyperparameters, such as learning rate and batch size, can significantly impact the performance of the neural network.
The optimization process can be formulated as follows: Loss Function: Mean Squared Error (MSE) or Mean Absolute Error (MAE) Optimization Algorithm: SGD or Adam Hyperparameters: Learning rate, batch size, number of epochs
| Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Learning Rate | 0.001 |
| Batch Size | 32 |
| Number of Epochs | 100 |
Applications and Future Implications

Neural collision detection using SDFs has a wide range of applications, including video games, virtual reality, and robotic motion planning. The ability to efficiently and accurately detect collisions enables the development of more realistic and immersive experiences. Additionally, the use of SDFs can enable the simulation of complex scenarios, such as deformable objects or fluids, which can be challenging to model using traditional methods.
Real-World Examples
Several real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of neural collision detection using SDFs. For instance, in the field of video games, neural collision detection can be used to simulate complex scenarios, such as character animation or vehicle collisions. In the field of virtual reality, neural collision detection can be used to enable more realistic and immersive experiences, such as simulating the motion of objects or characters.
- Video games: character animation, vehicle collisions
- Virtual reality: object motion simulation, character animation
- Robotic motion planning: collision avoidance, motion planning
What is the advantage of using SDFs in neural collision detection?
+The advantage of using SDFs in neural collision detection is that they enable the development of more efficient and accurate algorithms, which can be applied to a wide range of applications. SDFs provide a mathematical representation of 3D objects, which can be used to compute gradients and normals, making them an attractive choice for neural collision detection.
How is the neural network trained for neural collision detection?
+The neural network is trained using a dataset of 3D scenes and corresponding SDF values, which can be generated using various methods such as ray marching or sphere tracing. The network is optimized using an optimization algorithm, such as SGD or Adam, to minimize the difference between the predicted SDF values and the ground truth values.

