Reactor Pump Guide: Efficient Cooling Systems
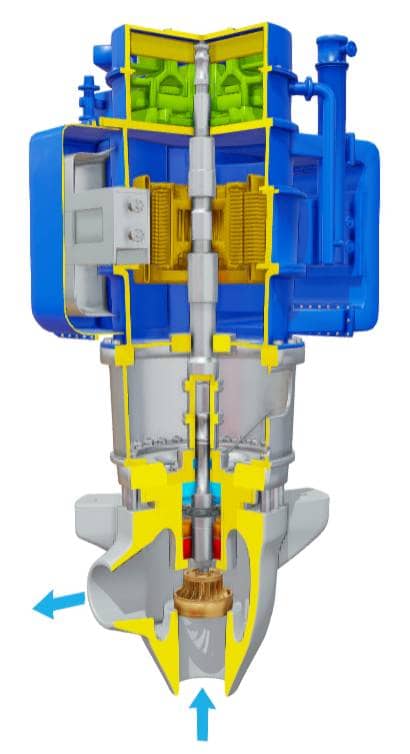

The reactor pump is a crucial component in nuclear power plants, responsible for circulating coolant through the reactor core to remove heat generated by nuclear fission. The efficiency of the cooling system is paramount to ensure safe and reliable operation of the reactor. In this guide, we will delve into the world of reactor pumps, exploring their design, operation, and significance in maintaining efficient cooling systems.
Introduction to Reactor Pumps
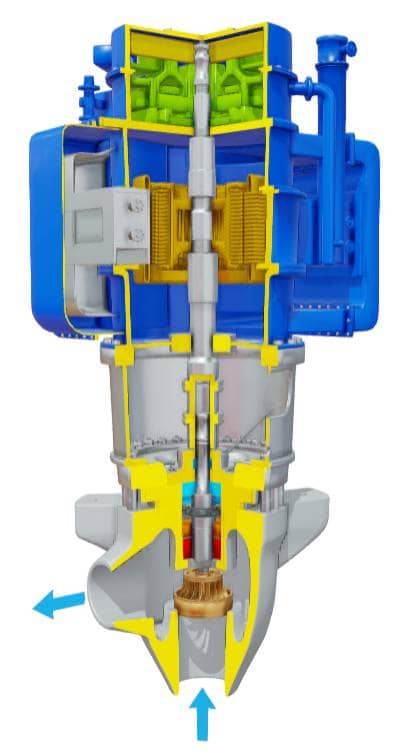

Reactor pumps are designed to handle the unique demands of nuclear reactor coolant systems. These pumps must be capable of withstanding high temperatures, pressures, and radiation levels while maintaining a reliable and efficient flow of coolant. The primary function of a reactor pump is to circulate coolant through the reactor core, transferring heat to a heat exchanger where it is dissipated to the environment. The most common types of reactor pumps used in nuclear power plants are centrifugal pumps and axial-flow pumps.
Design and Construction
The design and construction of reactor pumps are critical to their performance and reliability. These pumps are typically made from high-strength, corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or zirconium alloys. The pump’s impeller and diffuser are designed to optimize flow rates and minimize pressure drops, while the shaft seal and bearing systems are engineered to ensure reliable operation in high-radiation environments. The pump’s coolant channel is also carefully designed to minimize pressure drops and ensure efficient heat transfer.
| Pump Type | Flow Rate | Pressure Head |
|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal Pump | 10,000-50,000 gpm | 100-500 ft |
| Axial-Flow Pump | 50,000-200,000 gpm | 50-200 ft |

Operation and Maintenance

The operation and maintenance of reactor pumps are critical to ensuring efficient cooling systems. Pump performance is monitored continuously, with parameters such as flow rate, pressure head, and vibration levels tracked in real-time. Regular maintenance activities, such as inspection and testing, are performed to identify potential issues before they become major problems. The pump’s coolant channel is also subject to periodic cleaning and inspection to prevent corrosion and scaling.
Performance Optimization
Optimizing reactor pump performance is essential to maintaining efficient cooling systems. This can be achieved through a variety of means, including pump speed adjustment, impeller trimming, and diffuser optimization. Advanced technologies, such as computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and artificial intelligence (AI), can also be used to simulate pump performance and identify opportunities for improvement.
- Pump speed adjustment: adjusting the pump speed to optimize flow rates and pressure heads
- Impeller trimming: modifying the impeller design to improve efficiency and reduce energy consumption
- Diffuser optimization: optimizing the diffuser design to minimize pressure drops and improve heat transfer
What are the primary factors affecting reactor pump performance?
+The primary factors affecting reactor pump performance include the pump design, coolant type, flow rate, pressure head, and radiation levels. Other factors, such as pump speed, impeller design, and diffuser optimization, can also impact performance.
How often should reactor pumps be inspected and maintained?
+Reactor pumps should be inspected and maintained regularly, with the frequency of maintenance activities depending on the specific pump design, operating conditions, and regulatory requirements. Typically, pumps are inspected every 1-2 years, with major overhauls performed every 5-10 years.
Future Implications and Advancements
The reactor pump industry is continually evolving, with advances in technology and materials leading to more efficient and reliable pumps. The development of advanced materials and additive manufacturing techniques is expected to improve pump performance and reduce maintenance requirements. Additionally, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms can optimize pump operation and predict potential issues before they occur.
Next-Generation Reactor Pumps
Next-generation reactor pumps are being designed to meet the demands of future nuclear power plants, including small modular reactors (SMRs) and advanced pressurized water reactors (APWRs). These pumps will feature improved efficiency, increased reliability, and enhanced safety features, such as advanced coolant channel designs and passive safety systems. The use of advanced materials and additive manufacturing techniques will also enable the creation of complex pump geometries and optimized flow paths.

