Shelter Belts: Reduce Soil Erosion

Shelter belts, also known as windbreaks, are rows of trees or shrubs planted to reduce soil erosion, protect crops, and provide habitat for wildlife. These natural barriers have been used for centuries to mitigate the effects of wind and water erosion, which can lead to soil degradation and loss of fertile land. By reducing wind speed and trapping snow, shelter belts play a crucial role in preserving soil health and promoting sustainable agriculture. In this article, we will explore the benefits of shelter belts, their design and implementation, and their impact on reducing soil erosion.
Benefits of Shelter Belts

Shelter belts offer numerous benefits, including reduced soil erosion, improved soil health, and enhanced biodiversity. By blocking strong winds, shelter belts prevent soil particles from being lifted and carried away, reducing the risk of erosion and sedimentation in waterways. Additionally, shelter belts help to conserve soil moisture, reduce soil temperature fluctuations, and provide shade, which can lead to improved crop yields and reduced irrigation needs. Furthermore, shelter belts can serve as habitat corridors for wildlife, connecting fragmented habitats and promoting the movement of species.
Design and Implementation of Shelter Belts
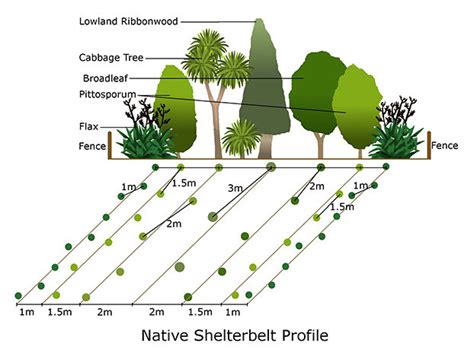
The design and implementation of shelter belts depend on various factors, including climate, soil type, and land use. Effective shelter belts typically consist of multiple rows of trees or shrubs, with a mix of species that provide a diverse range of benefits. The width and density of the shelter belt will depend on the wind speed and direction, as well as the type of crops being protected. For example, a shelter belt designed to protect a field of wheat may be narrower and less dense than one designed to protect a field of soybeans. The spacing and arrangement of the trees or shrubs will also impact the effectiveness of the shelter belt, with closer spacing providing greater protection from wind and erosion.
| Shelter Belt Design Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Width | Variable, depending on wind speed and direction |
| Density | Variable, depending on crop type and wind speed |
| Species mix | Diverse range of tree and shrub species |
| Spacing and arrangement | Close spacing for greater wind protection |
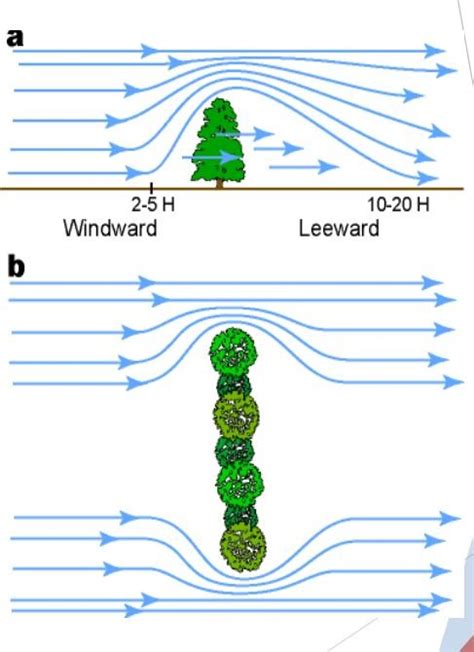
Impact of Shelter Belts on Soil Erosion
Shelter belts have been shown to significantly reduce soil erosion, with studies demonstrating a reduction in soil loss of up to 50%. By reducing wind speed and trapping snow, shelter belts help to prevent soil particles from being lifted and carried away, reducing the risk of erosion and sedimentation in waterways. Additionally, shelter belts can help to improve soil health by increasing soil organic matter, reducing soil compaction, and promoting soil biota. The impact of shelter belts on soil erosion can be measured using various metrics, including soil loss, sediment yield, and water quality.
- Soil loss reduction: up to 50% reduction in soil loss
- Sediment yield reduction: up to 70% reduction in sediment yield
- Water quality improvement: reduced turbidity, improved dissolved oxygen levels
Case Studies and Examples
Shelter belts have been successfully implemented in various regions and climates, providing valuable lessons and insights for farmers, land managers, and conservationists. For example, in the Great Plains of North America, shelter belts have been used to reduce soil erosion and protect crops from strong winds. In Australia, shelter belts have been used to reduce soil salinization and improve soil health. These case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of shelter belts in reducing soil erosion and promoting sustainable agriculture.
What are the key benefits of shelter belts?
+The key benefits of shelter belts include reduced soil erosion, improved soil health, and enhanced biodiversity. Shelter belts can also help to conserve soil moisture, reduce soil temperature fluctuations, and provide shade, leading to improved crop yields and reduced irrigation needs.
How are shelter belts designed and implemented?
+Shelter belts are designed and implemented based on various factors, including climate, soil type, and land use. Effective shelter belts typically consist of multiple rows of trees or shrubs, with a mix of species that provide a diverse range of benefits. The width and density of the shelter belt will depend on the wind speed and direction, as well as the type of crops being protected.
In conclusion, shelter belts are a valuable tool for reducing soil erosion and promoting sustainable agriculture. By designing and implementing effective shelter belts, farmers, land managers, and conservationists can help to protect soil health, reduce erosion, and promote biodiversity. As the global demand for food and fiber continues to grow, the importance of shelter belts in maintaining soil health and promoting sustainable agriculture will only continue to increase.