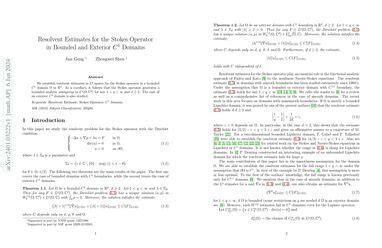
What Are Eigenvalues Of Stokes' Operator? A Clear Guide
The Stokes' operator, a fundamental concept in fluid dynamics, plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of viscous fluids. It is a linear operator that arises from the Stokes equations, which describe the motion of a viscous fluid in the low Reynolds number limit. The eigenvalues of the Stokes' operator are essential in analyzing the stability and behavior of fluid flows. In this article, we will delve into the world of eigenvalues of the Stokes' operator, providing a clear guide on what they are, how to calculate them, and their significance in fluid dynamics.
Introduction to Stokes’ Operator

The Stokes’ operator is a mathematical representation of the Stokes equations, which are a set of partial differential equations that describe the motion of a viscous fluid. The operator is defined as L = -μΔ + ∇p, where μ is the dynamic viscosity of the fluid, Δ is the Laplacian operator, and p is the pressure. The Stokes’ operator is used to study the behavior of fluid flows in various geometries, such as channels, pipes, and cavities. The eigenvalues of the Stokes’ operator are scalar values that represent the amount of change in the fluid flow when the operator is applied to it.
Calculating Eigenvalues of Stokes’ Operator
To calculate the eigenvalues of the Stokes’ operator, we need to solve the eigenvalue problem Lφ = λφ, where φ is the eigenfunction, and λ is the eigenvalue. The eigenfunction represents the shape of the fluid flow, while the eigenvalue represents the amount of change in the flow. The calculation of eigenvalues involves solving a set of partial differential equations, which can be done using various numerical methods, such as the finite element method or the spectral method. The finite element method is a popular choice for calculating eigenvalues of the Stokes’ operator, as it allows for the discretization of the domain into smaller elements, making it easier to solve the eigenvalue problem.
| Eigenvalue | Description |
|---|---|
| λ = 0 | Represents a steady-state flow |
| λ > 0 | Represents a decaying flow |
| λ < 0 | Represents a growing flow |

Significance of Eigenvalues in Fluid Dynamics

The eigenvalues of the Stokes’ operator have significant implications in fluid dynamics. They can be used to analyze the stability of fluid flows, predict the behavior of flows in different geometries, and optimize the design of fluid-based systems. The eigenvalues can also be used to study the transition from laminar to turbulent flow, which is a critical aspect of fluid dynamics. Furthermore, the eigenvalues can be used to develop control strategies for fluid flows, allowing for the manipulation of flow behavior in various applications, such as pipeline flow, ocean currents, and blood flow.
Applications of Eigenvalues in Fluid Dynamics
The eigenvalues of the Stokes’ operator have a wide range of applications in fluid dynamics, including:
- Predicting the behavior of fluid flows in complex geometries
- Analyzing the stability of fluid flows
- Optimizing the design of fluid-based systems
- Developing control strategies for fluid flows
- Studying the transition from laminar to turbulent flow
What are the eigenvalues of the Stokes' operator used for?
+The eigenvalues of the Stokes' operator are used to analyze the stability of fluid flows, predict the behavior of flows in different geometries, and optimize the design of fluid-based systems.
How are the eigenvalues of the Stokes' operator calculated?
+The eigenvalues of the Stokes' operator are calculated by solving the eigenvalue problem Lφ = λφ, where φ is the eigenfunction, and λ is the eigenvalue. This can be done using various numerical methods, such as the finite element method or the spectral method.
In conclusion, the eigenvalues of the Stokes’ operator are a fundamental concept in fluid dynamics, providing valuable insights into the behavior and stability of fluid flows. By understanding the eigenvalues of the Stokes’ operator, researchers and engineers can develop more efficient and effective fluid-based systems, and optimize the performance of existing systems. The significance of eigenvalues in fluid dynamics cannot be overstated, and their application will continue to play a critical role in advancing our understanding of fluid flows and their behavior.